Embarking on a culinary journey with i only eat fish, this comprehensive guide delves into the nutritional benefits, environmental implications, and delectable dishes that revolve around this aquatic delicacy.
From exploring the potential health advantages to understanding sustainable fishing practices, this discourse unravels the complexities of a fish-centric diet.
Nutritional Implications of a Fish-Only Diet
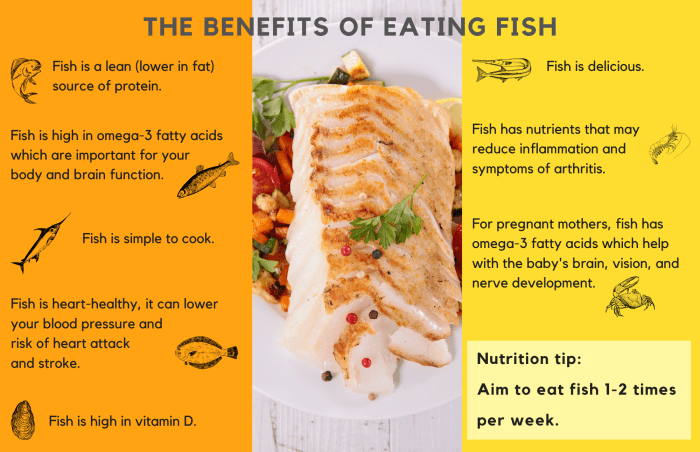
A fish-only diet can provide several nutritional benefits. Fish is a rich source of high-quality protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and various vitamins and minerals. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for heart and brain health, while vitamins and minerals support overall bodily functions.However, a fish-only diet may also lead to certain nutritional deficiencies.
If you’re a pescatarian on a budget, you know the struggle of finding affordable, delicious meals. That’s why we’ve rounded up a list of pescatarian recipes on a budget that will satisfy your cravings without breaking the bank. From hearty soups and stews to flavorful pasta dishes and grilled fish, there’s something for everyone in our collection.
Fish is not a significant source of carbohydrates, fiber, or vitamin C. Additionally, some fish species may contain high levels of mercury, which can be harmful if consumed in excess.It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before adopting a fish-only diet to ensure that all nutritional needs are met.
A healthcare professional can provide personalized advice based on individual health conditions and dietary requirements.
Potential Nutritional Deficiencies
A fish-only diet may lead to deficiencies in the following nutrients:
Carbohydrates
Fish does not provide carbohydrates, which are the body’s primary source of energy. A lack of carbohydrates can lead to fatigue, weakness, and impaired cognitive function.
Fiber
Fish is not a source of fiber, which is essential for digestive health and regularity. A lack of fiber can lead to constipation, bloating, and other digestive issues.
Vitamin C
Fish is not a significant source of vitamin C, which is an antioxidant that supports immune function and collagen production. A lack of vitamin C can lead to scurvy, a condition characterized by weakness, fatigue, and bleeding gums.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial before adopting a fish-only diet. A healthcare professional can:
- Assess individual nutritional needs based on age, health conditions, and activity level.
- Provide personalized dietary recommendations to ensure all nutritional requirements are met.
- Monitor blood levels to detect any potential nutrient deficiencies.
- Offer guidance on safe and sustainable ways to incorporate fish into a balanced diet.
Environmental Considerations of a Fish-Only Diet
Consuming fish has environmental implications that must be considered. Fish populations are finite, and overfishing can lead to the depletion of fish stocks and disruption of marine ecosystems.
Sustainable fishing practices aim to minimize the environmental impact of fishing by using selective gear, avoiding overfishing, and protecting critical habitats. These practices are crucial for maintaining healthy fish populations and preserving marine biodiversity.
Overfishing and Ethical Implications
Overfishing occurs when fish are harvested at a rate faster than they can reproduce. This can lead to population declines, disruption of food webs, and loss of biodiversity. The ethical implications of overfishing are significant, as it can threaten the livelihoods of fishers and compromise the health of marine ecosystems.
- Bycatch:Non-target species, such as dolphins, sea turtles, and seabirds, are often unintentionally caught in fishing gear, leading to mortality and population declines.
- Habitat destruction:Fishing practices, such as bottom trawling, can damage sensitive marine habitats, including coral reefs and seagrass beds, which are essential for fish reproduction and survival.
- Climate change:Rising ocean temperatures and acidification can impact fish populations and their habitats, exacerbating the effects of overfishing.
Adopting sustainable fishing practices and promoting responsible seafood consumption are essential steps towards mitigating the environmental impact of fish consumption and preserving the health of marine ecosystems.
Culinary Aspects of a Fish-Only Diet: I Only Eat Fish
A fish-only diet offers a wide range of culinary possibilities, with fish serving as a versatile and flavorful base for various dishes. By exploring different cooking techniques and incorporating fish into a balanced diet, individuals can enjoy the nutritional benefits of fish while also indulging in satisfying meals.
From grilling and baking to steaming and poaching, the cooking method can significantly impact the flavor and texture of fish. Grilling imparts a smoky and slightly charred flavor, while baking results in a tender and juicy texture. Steaming preserves the delicate flavors and nutrients of fish, and poaching creates a moist and flaky result.
Meal Ideas and Recipes
- Grilled Salmon with Lemon and Herbs: Grill salmon fillets seasoned with lemon juice, olive oil, salt, and pepper. Serve with roasted vegetables and a side of quinoa.
- Baked Cod with Parmesan Crust: Bake cod fillets topped with a mixture of grated Parmesan cheese, bread crumbs, and herbs. Serve with a side of roasted potatoes and steamed broccoli.
- Steamed Tilapia with Ginger and Soy: Steam tilapia fillets in a steamer basket over a mixture of ginger, soy sauce, and water. Serve with brown rice and a side of steamed bok choy.
- Poached Trout with Dill Sauce: Poach trout fillets in a court-bouillon made with white wine, herbs, and vegetables. Serve with a dill sauce made from Greek yogurt, dill, lemon juice, and salt.
Tips and Tricks
- Use fresh, high-quality fish for the best flavor and texture.
- Season fish generously with salt and pepper to enhance its natural flavors.
- Cook fish to the proper internal temperature to ensure it is cooked through but not overcooked.
- Experiment with different marinades and sauces to add variety to your fish dishes.
- Pair fish with complementary sides such as vegetables, grains, and fruits to create a balanced meal.
Health Benefits of a Fish-Only Diet
Consuming fish is widely recognized for its numerous health benefits, and a fish-only diet can amplify these advantages. Scientific evidence consistently demonstrates the positive impact of fish consumption on cardiovascular health. The omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), play a crucial role in reducing the risk of heart disease.
Cardiovascular Health
Fish consumption has been associated with a lower risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and arrhythmias. Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce blood pressure, improve blood flow, and prevent the formation of blood clots. They also increase the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, the “good” cholesterol that helps remove excess cholesterol from the body.
Chronic Disease Risk Reduction
Studies suggest that a fish-only diet may reduce the risk of certain chronic diseases, including cancer and dementia. Omega-3 fatty acids have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may protect against the development and progression of these diseases. Fish is also a good source of vitamin D, which is essential for bone health and may play a role in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Fish is a rich source of anti-inflammatory compounds, including omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and selenium. These compounds help reduce inflammation throughout the body, which is associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, arthritis, and asthma.
Anti-inflammatory diets have also been shown to improve overall well-being, reduce pain, and enhance cognitive function.
Potential Drawbacks of a Fish-Only Diet
While a fish-only diet can provide numerous health benefits, it also has some potential drawbacks that need to be considered. These include the accumulation of mercury, the risk of iodine deficiency, and the challenges of adhering to such a restrictive diet in different cultural and geographical contexts.
Mercury Accumulation
Fish is a major source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart and brain health. However, some types of fish, such as tuna, swordfish, and shark, can contain high levels of mercury. Mercury is a neurotoxin that can damage the brain and nervous system, especially in developing fetuses and young children.
Pregnant women, women who are planning to become pregnant, and young children should limit their intake of fish that are high in mercury. They should also choose fish that are low in mercury, such as salmon, shrimp, and tilapia.
Iodine Deficiency
Iodine is an essential mineral that is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, growth, and development. Fish is a good source of iodine, but a fish-only diet may not provide enough iodine to meet the body’s needs.
Iodine deficiency can lead to a number of health problems, including hypothyroidism, which can cause fatigue, weight gain, and depression. It is important to include other sources of iodine in the diet, such as iodized salt, dairy products, and eggs.
Challenges of Adhering to a Fish-Only Diet
A fish-only diet can be challenging to adhere to in different cultural and geographical contexts. In some cultures, fish is not a traditional part of the diet. In other areas, fish may be expensive or difficult to obtain.
It is important to find a balance between eating a healthy diet and adhering to a fish-only diet. If you are considering a fish-only diet, it is important to talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian to make sure that you are getting all the nutrients you need.
Alternative Dietary Options to a Fish-Only Diet

A fish-only diet, while providing essential nutrients, may not be suitable for everyone due to personal preferences, health concerns, or ethical reasons. Fortunately, there are various alternative dietary options that can offer similar nutritional benefits without relying solely on fish consumption.
Adopting a pescatarian diet doesn’t have to break the bank. Whether you’re new to the pescatarian lifestyle or simply looking for budget-friendly meal ideas, we’ve got you covered. Explore our comprehensive guide to pescatarian recipes on a budget that won’t compromise your taste buds or your wallet.
Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets, including vegan and vegetarian diets, emphasize the consumption of plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. These diets are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and essential vitamins and minerals.
Vegetarian Diets, I only eat fish
Vegetarian diets exclude meat, poultry, and fish but allow the consumption of dairy products and eggs. They provide a good source of protein from plant-based sources such as beans, lentils, and tofu. Vegetarian diets have been associated with lower risks of chronic diseases like heart disease and certain types of cancer.
Role of a Registered Dietitian or Other Qualified Healthcare Professional
Consulting with a registered dietitian or other qualified healthcare professional is crucial when considering any significant dietary changes. These professionals can provide personalized guidance, assess individual nutritional needs, and ensure a balanced and sustainable diet that meets specific health goals and preferences.
Final Wrap-Up

Whether seeking to improve cardiovascular health, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, or simply indulge in culinary delights, i only eat fish offers a thought-provoking exploration into the world of pescatarianism. By embracing a balanced approach and considering environmental sustainability, individuals can harness the power of fish for optimal well-being.
FAQ Overview
Is a fish-only diet nutritionally adequate?
While fish is a nutrient-rich food, a fish-only diet may lack certain essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, and calcium. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before adopting such a restrictive diet.
What are the environmental concerns associated with a fish-only diet?
Overfishing can deplete fish populations and harm marine ecosystems. Sustainable fishing practices, such as choosing responsibly sourced fish and reducing seafood consumption, are essential for preserving ocean health.
Can a fish-only diet be flavorful and versatile?
Absolutely! Fish offers a wide range of flavors and textures, making it a culinary chameleon. From grilling and baking to steaming and frying, there are countless ways to prepare fish, ensuring a diverse and delectable dining experience.